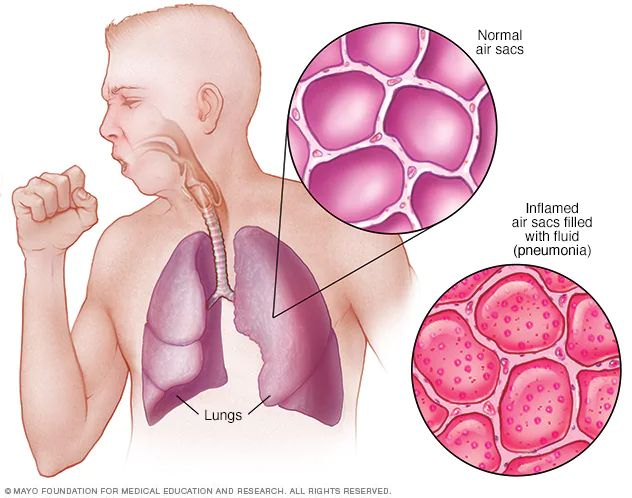
Pneumonia is a possibly life-threatening disease that arouses the lungs’ discuss sacs (alveoli), making breathing challenging and getting adequate oxygen. This aggravation causes the discussed sacs to fill with liquid, discharge, or other flotsam and jetsam, leading to impeded gas trade and diminished body oxygenation. If this contamination influences both lungs at that point it is called double pneumonia.
Reference: Pneumonia
Causes of Pneumonia
Pneumonia is caused by an assorted run of pathogens, including microscopic organisms, infections, parasites, and parasites. Bacterial pneumonia is the most common sort with Streptococcus pneumoniae being the driving guilty party. Other microbes like Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa can trigger pneumonia.
Viral pneumonia, on the other hand, is regularly caused by the flu infection, Respiratory Syncytial Infection (RSV), and Adenovirus. Rhinovirus, Coronavirus (COVID-19), Cytomegalovirus (CMV), and Herpes simplex infection (HSV) can also lead to viral pneumonia.
Fungal pneumonia is ordinarily caused by Pneumocystis jirovecii, Histoplasma capsulatum, Cryptococcus neoformans, Aspergillus fumigatus, and Candida albicans. These parasites frequently target people with debilitated safe systems.
In expansion to these pathogens, pneumonia can also result from parasitic diseases, such as Plasmodium falciparum (intestinal sickness) and Toxoplasma gondii. Introduction to poisonous substances like chlorine gas or hydrocarbon ingestion can moreover lead to chemical pneumonia. Besides, therapeutic methods like ventilation can increase the chance of creating pneumonia. Radiation introduction is another uncommon cause of pneumonia.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
Pneumonia typically presents with a persistent cough, often accompanied by fever, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. Fatigue, sweating, and chills are also common symptoms experienced by individuals with pneumonia. In severe cases, pneumonia can lead to confusion, disorientation, and extreme difficulty breathing, which can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Children with pneumonia may exhibit rapid breathing, wheezing, and pauses in breathing, while older adults may experience confusion, disorientation, and a decline in functional abilities. Abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea can also occur, especially in children.
If symptoms worsen or severe symptoms develop, such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, confusion, or severe headache, immediate medical attention is crucial to prevent life-threatening complications like respiratory failure, sepsis, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Reference: Symptoms
Diagnosis of Pneumonia
Diagnosing pneumonia includes a combination of physical examination, imaging tests, and research facility tests.
Physical Examination:
A healthcare supplier will conduct an intensive physical examination to survey lung sounds, breathing rate, and general well-being. They may utilize a stethoscope to distinguish anomalous sounds, such as crackles or wheezes, and check for signs of respiratory distress.
Imaging Tests:
Chest X-rays are the most commonly utilized imaging test to analyze pneumonia, uncovering regions of solidification in the lungs. Computed Tomography (CT) filters may be utilized to affirm the determination, recognize complications, or directly encourage procedures.
Laboratory Tests:
Blood societies are utilized to distinguish microscopic organisms in the blood and illuminate anti-microbial treatment. Sputum examination looks at bodily fluid from the lungs to identify microbes, infections, or organisms. A total blood number (CBC) checks for signs of disease, whereas blood chemistry tests survey kidney and liver work, electrolyte levels, and other variables.
Additional Symptomatic Tests:
Bronchoscopy outwardly analyzes the aviation routes and collects tests for culture or biopsy. A lung biopsy looks at lung tissue for signs of pneumonia or other conditions. Beat oximetry measures oxygen immersion in the blood.
Treatment of Pneumonia
Pneumonia treatment shifts depending on the fundamental cause and seriousness of the infection.
For bacterial pneumonia, anti-microbial treatment is the essential treatment approach. The particular anti-microbial utilized depends on the sort of microscopic organisms causing the contamination. Treatment regularly keeps going between 5-14 days, depending on the seriousness of the ailment and the patient’s response.
In cases of viral pneumonia, antiviral solutions may be endorsed to offer assistance oversee side effects, and abbreviate the term of the sickness. The sort of antiviral pharmaceutical utilized depends on the particular infection causing the infection.
Fungal pneumonia requires antifungal medicine, which can take a few weeks to months to successfully treat the infection.
In expansion to focus on medications, steady care is pivotal for overseeing pneumonia indications and advancing recuperation. This includes:
- Oxygen treatment to guarantee satisfactory oxygen levels
- Hydration to avoid dehydration
- Rest to permit the body to recover
- Torment administration to lighten chest torment and discomfort
- Bronchodilators to open aviation routes and move forward breathing
Reference: Treatment of Pneumonia
Complications
Pneumonia can cause severe complications, including respiratory failure that threatens life. Inflammation and fluid buildup in the lungs reduce oxygen supply, leading to Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS). Sepsis also occurs when the body’s inflammatory response to infection spirals out of control, causing widespread inflammation and organ damage. Bacterial infections can create pockets of pus in the lungs, known as lung abscesses. Excess fluid accumulates in the chest cavity, impairing breathing and leading to pleural effusion. Moreover, pneumonia can lead to cardiac arrest, septic shock, kidney failure, and bloodstream infections like bacteremia. Early medical intervention is crucial to prevent and manage these complications effectively.
Prevention
Avoiding pneumonia requires a comprehensive approach that includes different procedures. Firstly, immunizations such as the pneumococcal conjugate antibody offer pivotal security against pneumonia. In addition, great cleanliness hones like handwashing and mask-wearing are fundamental to avoid the spread of contamination. Besides, stopping smoking essentially decreases the chance of creating pneumonia, as it debilitates the lungs’ guards. In expansion, keeping up a solid way of life through customary workouts, adjusted eating, and satisfactory rest is crucial to boost the resistant framework. Subsequently, by receiving these preventive measures, people can considerably lower their hazard of creating pneumonia. By taking proactive steps, individuals can protect themselves and others from this possibly life-threatening malady.

Reference: Preventive Measures
Taking proactive measures to avoid respiratory contaminations, such as bronchitis, is pivotal to shielding one’s well-being. By embracing a comprehensive approach that incorporates immunization, great cleanliness hones, smoking cessation, and a sound way of life, people can altogether decrease their chance of creating this possibly life-threatening condition. Keep in mind that a solid resistant framework is the best defense against respiratory sicknesses, and by prioritizing well-being and wellness, individuals can breathe simply and live life to the fullest.