Hepatitis(liver infection) refers to liver inflammation, which can result from various factors. These include viral infections, exposure to harmful chemicals and drugs, excessive alcohol consumption, genetic disorders, and autoimmune responses where the immune system mistakenly targets the liver. The condition can manifest in two primary forms: acute characterized by sudden onset and resolution, and chronic a long-term condition marked by subtle symptoms and progressive liver damage.
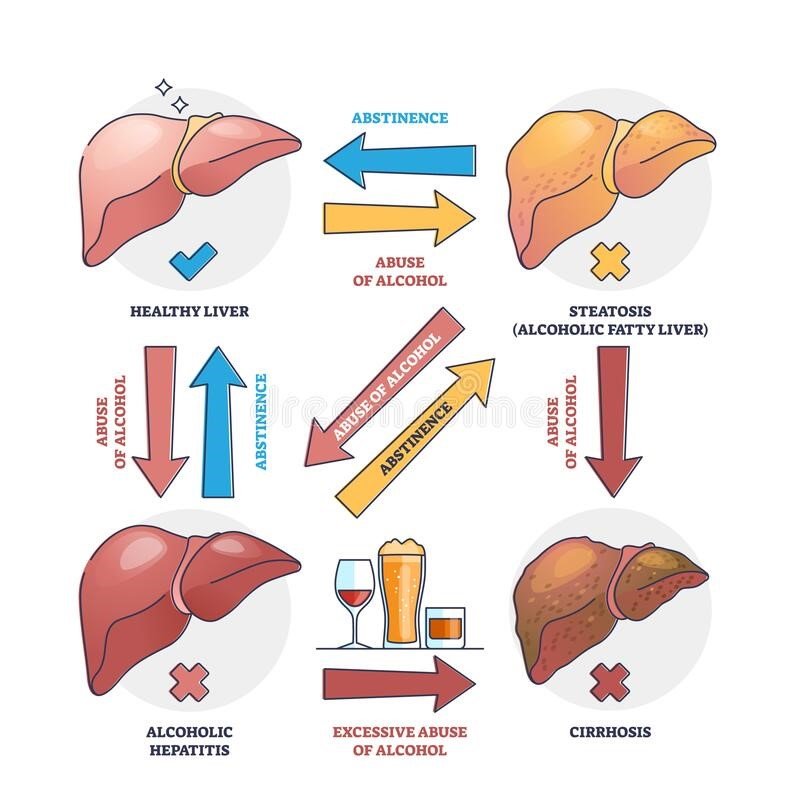
Reference: Hepatitis
Causes and Risk Factors
Viral Hepatitis:
- Hepatitis A: Contaminated food and water, poor sanitation, and close contact with infected person
- Hepatitis B: Infected bodily fluids, sexual contact, sharing needles, and mother-to-child transmission
- Hepatitis C: Infected bodily fluids, sharing needles, and less commonly through sexual contact
- Hepatitis D: Infected bodily fluids and sharing needles (only affects those with hepatitis B)
- Hepatitis E: Contaminated food and water, especially undercooked pork and wild game
Non-Viral Hepatitis:
- Alcohol-related hepatitis: Excessive alcohol consumption
- Toxic hepatitis: Exposure to toxic substances, such as chemicals and drugs
- Autoimmune hepatitis: Abnormal immune response attacking liver cells
- Genetic disorders: Certain genetic conditions, such as Wilson’s disease and hemochromatosis
Risk Factors:
- Age: Certain types of hepatitis affect specific age groups (e.g., hepatitis A affects children and young adults)
- Travel: Visiting areas with high hepatitis prevalence
- Sexual activity: Unprotected sex with infected partners
- Sharing needles: Injecting drugs or sharing needles with infected individuals
- Poor hygiene: Inadequate sanitation and handwashing
- Weakened immune system: Conditions like HIV/AIDS, cancer, or taking immunosuppressive drugs
- Family history: Having a family member with hepatitis or liver disease
Symptoms and Diagnosis
An person tainted with hepatitis may show a extend of indications, counting weakness, reduced craving, queasiness, heaving, stomach distress, dark-colored pee, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes). In any case, in a few occurrences, hepatitis may not show discernible indications, especially amid the introductory stages.
To analyze hepatitis, healthcare experts ordinarily utilize a combination of physical examination, restorative history assessment, and research facility tests. Blood tests can recognize the nearness of hepatitis infections, liver harm, and lifted liver chemicals. Imaging tests, such as ultrasound or liver biopsy, may moreover be utilized to survey liver harm and affirm the conclusion. In certain cases, extra tests may be fundamental to run the show out other conditions that may be causing comparative symptoms.
Early discovery and treatment altogether affect the result for people with hepatitis. If indications are display or presentation to hepatitis has happened, counseling a healthcare proficient for legitimate assessment and care is crucial.
Types of Hepatitis
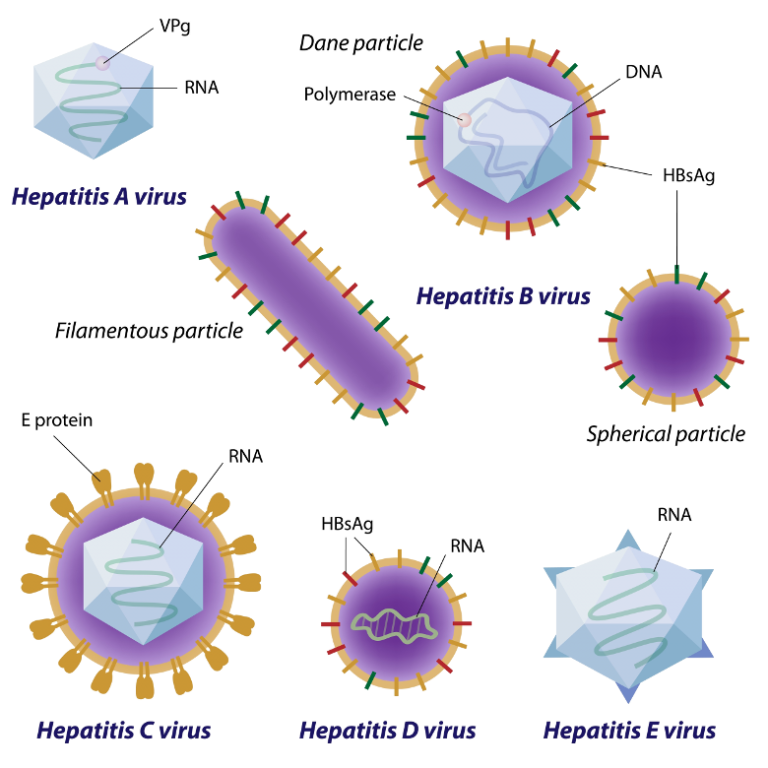
1. Hepatitis A: This sort is caused by the hepatitis A infection (HAV) and is ordinarily transmitted through sullied nourishment and water sources, or near contact with an contaminated individual.
2. Hepatitis B: The hepatitis B infection (HBV) causes this sort, which is spread through contaminated real liquids, sexual contact, sharing of needles, or from mother to child amid childbirth.
3. Hepatitis C: This sort is fundamentally caused by the hepatitis C infection (HCV) and is transmitted through tainted substantial liquids and sharing of needles.
4. Hepatitis D: The hepatitis D infection (HDV) causes this sort, which as it were influences people as of now contaminated with hepatitis B.
5. Hepatitis E: This sort is caused by the hepatitis E infection (HEV) and is ordinarily spread through sullied nourishment and water sources, especially undercooked pork and wild game.
6. Alcoholic Hepatitis: Intemperate liquor utilization leads to this sort, causing liver aggravation and damage.
7. Immune system Hepatitis: In this sort, the resistant framework erroneously assaults liver cells, driving to aggravation and damage.
8. Poisonous Hepatitis: Presentation to destructive substances, such as chemicals or drugs, causes this sort, driving to liver damage.
Reference: Different Types
Treatment and Management
Treatment for hepatitis depends on the sort and seriousness of the disease. For intense hepatitis, treatment ordinarily centers on soothing indications and supporting liver wellbeing through rest, hydration, and nourishment. In a few cases, antiviral medicines may be endorsed to offer assistance clear the virus.
For persistent hepatitis, treatment points to moderate illness movement, decrease liver harm, and anticipate complications. Antiviral medicines, such as intergalactic and direct-acting antivirals, may be utilized to smother viral replication. In progressed cases, liver transplantation may be necessary.
Lifestyle adjustments play a significant part in overseeing hepatitis. People with hepatitis ought to dodge liquor utilization, keep up a solid weight, and follow to a adjusted count calories. Standard work out and stretch administration can moreover offer assistance back liver health.
In expansion to therapeutic treatment, people with hepatitis can take steps to avoid transmission and ensure others. This incorporates practicing secure sex, maintaining a strategic distance from sharing needles or individual things, and getting inoculated against hepatitis A and B.
Early location and treatment are basic in overseeing hepatitis and anticipating long-term liver harm. If you’re encountering side effects or have been uncovered to hepatitis, counsel a healthcare proficient for legitimate assessment and care.
Complications and Long-term Effects
Liver Disappointment: If cleared out untreated, hepatitis can advance to liver disappointment, a life-threatening condition requiring liver transplantation.
Liver Cancer: Hepatitis B and C increment the chance of liver cancer, emphasizing the require for early location and treatment.
Kidney Harm: Also, liver infection can harm kidneys, driving to kidney illness and advance complicating in general health.
Liver Harm: Hepatitis can cause liver harm, driving to liver cirrhosis, a condition where scarring and liver harm disable liver function.
Thyroid Clutters: In addition, liver infection can trigger thyroid issues, highlighting the significance of observing thyroid function.
Immune system Maladies: Hepatitis can moreover trigger immune system illnesses, where the resistant framework erroneously assaults solid tissues.
Unremitting Aggravation: Besides, hepatitis can lead to inveterate irritation, causing progressing liver harm and expanding the hazard of complications.
Lack of healthy sustenance: Lacking nourishment can worsen liver infection indications, making it basic to keep up a adjusted diet.
Mental Wellbeing: At last liver infection can take a toll on mental wellbeing, causing uneasiness, misery, and stress.
Prevention and Vaccination
- Immunization: Secure yourself from liver illness by getting inoculated against Hepatitis A and B, a significant step in prevention.
- Secure Sex Hones: Decrease the chance of transmitting liver contaminations like Hepatitis B and C by practicing secure sex, counting utilizing condoms.
- Sterile Hardware: Anticipate the spread of liver diseases by maintaining a strategic distance from shared needles and utilizing sterile equipment.
- Great Cleanliness: Keep up great cleanliness, such as washing hands routinely, to avoid the transmission of liver contaminations like Hepatitis A and E.
- Nourishment Security: Handle nourishment securely by maintaining a strategic distance from undercooked or crude nourishments, particularly pork and wild amusement, to avoid Hepatitis E transmission.
- Customary Screening: Distinguish liver contaminations early and avoid long-term harm through standard screening and testing.
- Sound Way of life: Bolster liver wellbeing by embracing a solid way of life, counting a adjusted eat less and standard exercise.
- Mindfulness and Instruction: Remain educated and teach others almost liver contaminations to anticipate transmission and decrease stigma.
Reference: Prevention
Liver infection is a genuine and possibly life-threatening condition that can be avoided and treated with legitimate measures. By getting immunized against liver contaminations, practicing secure sex, dodging shared needles, keeping up great cleanliness, taking care of nourishment securely, taking travel safeguards, experiencing standard screening, embracing a solid way of life, and remaining educated, people can altogether diminish their chance of liver infection and secure their in general wellbeing. It is basic to raise mindfulness and teach others almost liver contaminations to avoid transmission and decrease disgrace. By taking these steps, we can work towards a future where liver infection is uncommon and reasonable, and where people can live sound and satisfying lives.