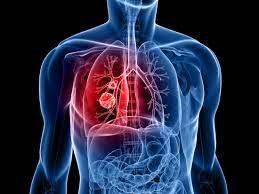
Lung cancer is a formidable health threat, responsible for a significant number of cancer-related deaths globally. This devastating disease arises when rogue cells in the lung tissue begin to proliferate uncontrollably, forming tumors that can infiltrate surrounding areas and metastasize to distant parts of the body. Lung cancer’s reach is indiscriminate, affecting individuals of all ages and health backgrounds. To combat this disease effectively, it’s essential to grasp its underlying risk factors, recognize its often subtle symptoms, and understand the array of treatment options available. By exploring the complexities of lung cancer and examining the latest developments in prevention, diagnosis, and care, we can work towards improving outcomes and saving lives.
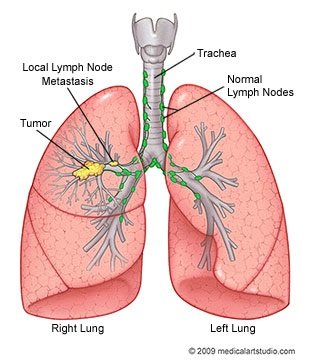
Reference: Lung Cancer
Risk Factors
Lung cancer chance variables can be categorized into modifiable and non-modifiable components. Modifiable variables incorporate smoking and tobacco utilization, which altogether increases the hazard of lung cancer. Introduction to used smoke, discuss contamination, and word related carcinogens like asbestos and diesel debilitate moreover contribute to the chance. Furthermore, radon presentation in homes and buildings can pose a noteworthy risk. By tending to these modifiable variables, people can diminish their chance of developing lung cancer.
On the other hand, non-modifiable variables such as family history and hereditary changes, like EGFR and ALK, can increase an individual’s defenselessness to lung cancer. Age is moreover a non-modifiable figure, as the chance of lung cancer increments with age. Besides, past radiation treatment to the chest can moreover raise the risk.
Other variables can moreover contribute to an individual’s general hazard of creating lung cancer. Introduction to harmful substances like arsenic, chromium, and nickel can increase the hazard. Besides, certain restorative conditions like human immunodeficiency infection (HIV) contamination, unremitting obstructive aspiratory infection (COPD), and tuberculosis (TB) can moreover play a part in expanding the chance of lung cancer. Understanding these hazard components can offer assistance to people to take preventive measures and look for therapeutic consideration if vital.
Lung Cancer Symptoms
Lung cancer can manifest with a range of symptoms, including:
- Persistent and unexplained coughing or wheezing which may worsen over time.
- Chest discomfort or pain that intensifies with deep breathing, coughing, or physical activity.
- Unexplained shortness of breath or feeling winded, even when engaging in light activities.
- Coughing up blood or rust-colored mucus which can be a sign of advanced disease.
- Fatigue or extreme tiredness that persists despite rest.
- Unintentional weight loss due to decreased appetite or difficulty eating.
- Recurring respiratory infections, such as pneumonia or bronchitis.
- Swelling in the face, arms, or neck due to fluid buildup.
- Hoarseness or a raspy voice which can be a sign of tumor growth.
- Pain or discomfort in the shoulders, arms, or back, which can radiate from the chest.
- Weakness or numbness in the arms or legs, which can indicate nerve damage.
- Difficulty swallowing or feeling like food is getting stuck in the throat.
- Coughing up yellow or green mucus, which can be a sign of infection.
- Noticing a lump or nodule in the neck or chest area, which can be a sign of advanced disease.
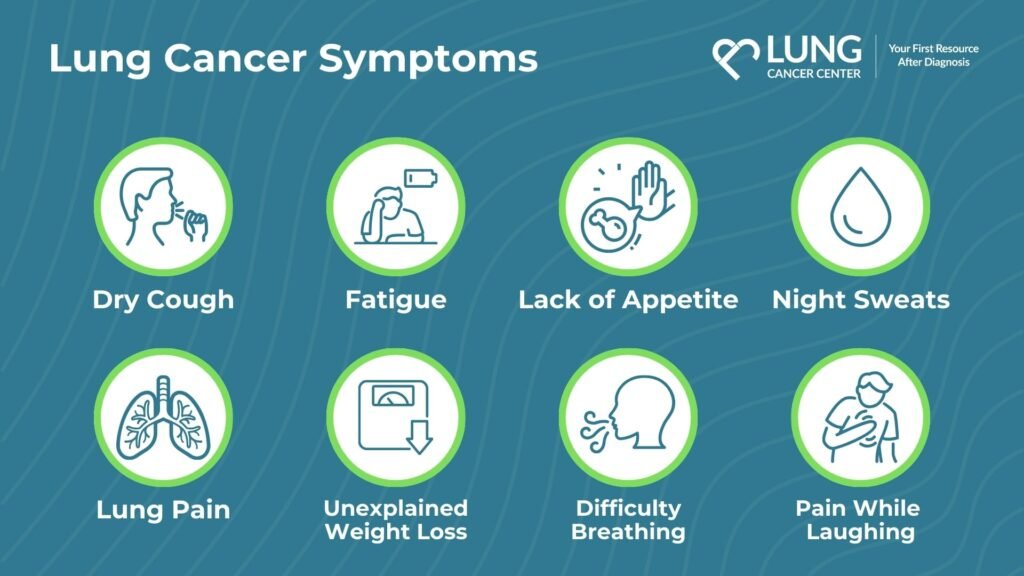
Reference: Symptoms
Diagnosis
Diagnosing lung cancer involves a multifaceted approach, combining imaging tests like chest X-rays, CT scans, PET scans, and MRI scans to visualize the lungs and identify abnormalities, with biopsy procedures such as fine-needle aspiration, core needle biopsy, surgical biopsy, and bronchoscopic biopsy to confirm cancer cells through tissue samples. Additionally, blood tests like complete blood counts and blood chemistry tests assess overall health and detect potential biomarkers while pulmonary function tests like spirometry and diffusion capacity tests measure lung function and capacity. Further tests, including sputum cytology and thoracentesis, may also be conducted to gather more information, and a healthcare professional will interpret the results to confirm a lung cancer diagnosis, stage the disease, and guide treatment decisions, developing an effective treatment plan tailored to each patient’s unique needs.
Treatment Options
Surgical intercessions for lung cancer point to expel the tumor and encompass solid tissue. Strategies incorporate wedge resection, segmental resection, lobectomy, and pneumonectomy, each shifting in scope. Surgery may be an alternative for localized cancer, and chemotherapy or radiation treatment might be utilized sometime recently or after surgery to improve results. Radiation treatment utilizes capable vitality bars to annihilate cancer cells, regularly combined with chemotherapy for ideal outcomes. Chemotherapy utilizes solid solutions to combat cancer, managed through veins or pills, and may be utilized alone or in conjunction with radiation treatment. Stereotactic body radiotherapy is strongly, focused on radiation treatment appropriate for little lung cancers or those that have spread. Focused on treatment employments medications that assault particular chemicals in cancer cells, whereas immunotherapy saddles the safe framework to murder cancer cells. Palliative care alleviation from torment and side effects, moving forward the quality of life for patients with genuine sicknesses, and can be utilized concurrently with cancer medications.
Lung Cancer Prevention
Anticipating lung cancer includes a combination of way of life changes and dodging destructive exposures. Stopping smoking and controlling clear of smoke are pivotal, as tobacco utilization is the driving cause of lung cancer. Also, restricting introduction to carcinogens like asbestos and radon can essentially decrease the hazard of creating the illness. A sound eater less wealthy in natural products and vegetables, customary workout, and getting inoculated against infections like HPV and Hepatitis B can moreover offer assistance to avoid lung cancer.
Early location is basic in treating lung cancer, and screening tests like low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) can recognize high-risk people. Chest X-rays, sputum cytology, and biomarker testing can moreover identify cancer cells or anomalies. Imaging tests like PET and MRI checks may be utilized to affirm analysis. Customary well-being check-ups and meetings with a healthcare supplier are basic for checking indications and surveying hazard components, such as family history and natural exposures. By taking proactive steps towards anticipation and early discovery, people can altogether diminish their hazard of creating lung cancer.
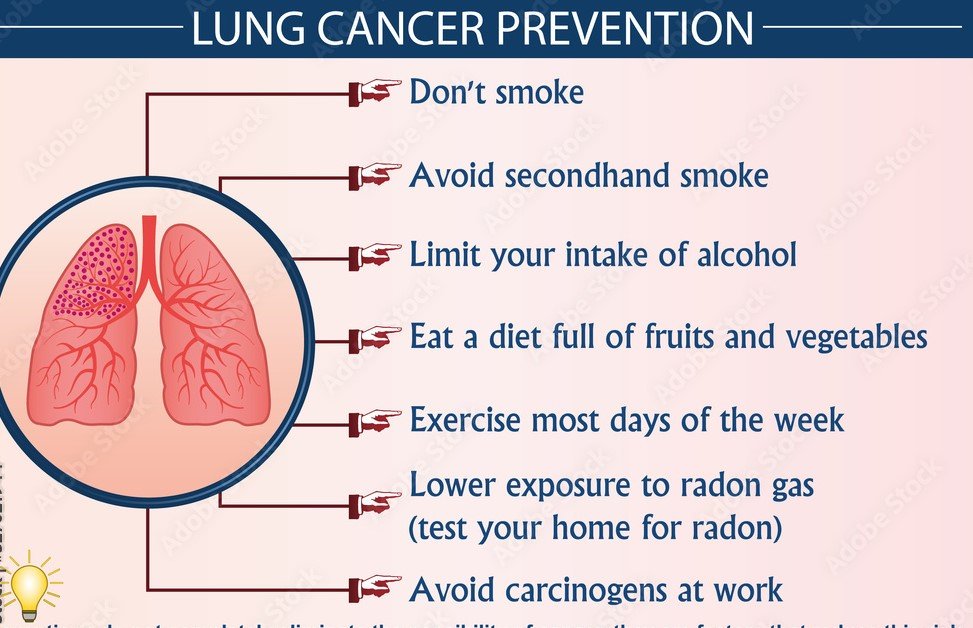
Reference: Prevention
lung cancer is an intricate and dynamic condition that necessitates a multifaceted approach to treatment and management. A range of options, including surgical interventions, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and precision medicine, offer patients various pathways to recovery. Ongoing research and clinical trials further expand the possibilities for effective care. Emphasizing prevention and early detection through screening and risk assessment is vital in enhancing patient outcomes. By taking an informed and proactive stance, individuals can assume control of their health and contribute to a future where lung cancer is increasingly manageable and treatable. Through continued advancements in medical science and a patient-centric approach, hope and healing are within reach for those impacted by this disease.