Hemophilia is an uncommon and acquired condition that influences the blood’s capacity to shape clots, leading to delayed death or simple bruising. This hereditary clutter is characterized by insufficiency or glitch of basic proteins, known as clotting variables, which play a pivotal part in blood coagulation preparation. Hemophilia A need or brokenness of clotting causes a calculate VIII, whereas an insufficiency or brokenness of clotting figure IX causes hemophilia B. As a result, people with this bleeding disorder may encounter unconstrained death or dying taking after wounds or surgical methods, which can be serious and possibly life-threatening if cleared out untreated.
Reference: Hemophilia
Types of Hemophilia
Hemophilia is classified into three essential categories, each recognized by the particular clotting figure’s lack or dysfunction.
Type A
Hemophilia A, the most predominant frame, accounts for around 80% of cases and is characterized by a lack or breakdown of clotting Figure VIII. The seriousness of Hemophilia A can change broadly, extending from mellow to severe.
Type B
Hemophilia B, moreover known as Christmas Illness, is less common, influencing around 20% of people with hemophilia. This sort is caused by a lack or brokenness of clotting Figure IX and, like Hemophilia A, can show an extend of severity.
Type C
Hemophilia C, or Rosenthal Disorder, is an uncommon shape of the clutter, coming about from insufficiency or brokenness of clotting calculate XI. Regularly, Hemophilia C is milder than the other two types.
In expansion to these essential categories, there are other uncommon shapes of hemophilia, counting procured hemophilia, which occurs afterward in life, frequently due to basic therapeutic conditions or cancer. In a few cases, people with hemophilia A or B may too create inhibitors, which are antibodies that meddled with clotting variables. Mellow hemophilia, characterized by negligible indications, may as it were end up clear amid surgical methods or traumatic occasions.
Causes of Hemophilia
Hereditary Causes:
- Acquired quality transformations change clotting variables VIII and IX, driving to hemophilia A and B.
- Unconstrained quality transformations can also cause this bleeding disorder.
- Changes in the clotting figure XI quality cause hemophilia C.
Inheritance Patterns:
- The X chromosome carries the qualities for hemophilia A and B, essentially influencing males.
- Females can carry the transformed quality and pass it to their children.
- Hemophilia C influences both guys and females similarly due to its autosomal latent legacy pattern.
Acquired Causes:
- Immune system disarranges trigger the generation of antibodies against clotting factors.
- Certain cancers, drugs, and contaminations can also lead to the advancement of antibodies against clotting factors.
- Age and family history increase the chance of creating hemophilia.
Additional Hazard Factors:
- A family history of hemophilia increases the probability of acquiring the condition.
- Side effects may not show up until afterward in life, indeed if the condition is display at birth.
- Certain ethnic bunches, such as Caucasians, are more likely to create hemophilia A and B.
Symptoms
Characteristic Signs:
- Uncontrolled bleeding or discoloration due to minor injuries
- Recurring joint or muscle bleeding, leading to pain and swelling
- Joint stiffness or limited mobility from repeated bleeding episodes
- Frequent or prolonged bleeding from the nose or gums
- Excessive menstrual bleeding in females
Severe Indications:
- Life-threatening bleeding into critical organs, such as the brain or abdomen
- Chronic joint pain or disability from repeated bleeding
- Increased susceptibility to infections
- Organ damage from recurrent bleeding episodes
Emergency Warning Signs:
- Sudden, severe headache or stiff neck, potentially indicating bleeding in the brain
- Vomiting, confusion, or altered mental state
- Difficulty speaking, swallowing, or experiencing weakness/numbness in the face, arm, or leg
- Severe abdominal pain or rapid heartbeat/palpitations, potentially indicating internal bleeding
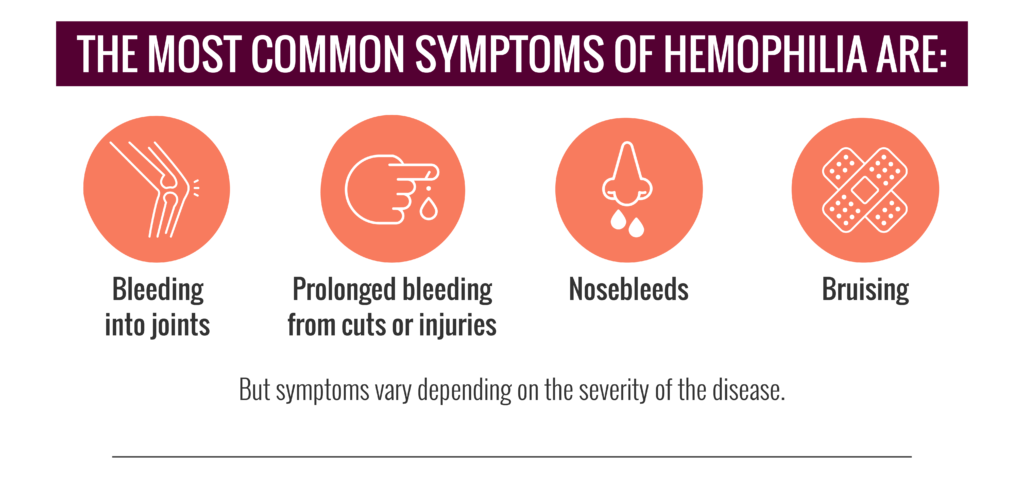
Reference: Warning Signs
Diagnosis of Hemophilia
Diagnosing hemophilia includes a comprehensive approach that incorporates a careful restorative history, physical examination, and research facility tests. The handle starts with a survey of individual and family therapeutic history to recognize any dying clutters. A physical examination is at that point conducted to see for signs of death, bruising, or joint harm. Blood tests are moreover significant in diagnosing this disorder, as they degree the levels and movement of clotting components, counting calculate VIII and figure IX. These tests incorporate a total blood tally, prothrombin time, fractional thromboplastin time, and clotting calculation measures. Also, hereditary testing can offer assistance in distinguishing acquired quality changes that cause inherited bleeding condition. In a few cases, imaging considers like X-rays or MRIs may be utilized to survey joint harm. A conclusive conclusion of hemophilia is made when moo clotting figure levels, delayed dying time, and characteristic indications such as joint dying and simple bruising are shown, along with a positive family history.
Treatment and Management
Successful administration of hemophilia requires a multifaceted approach that includes different techniques to avoid and control dying scenes, lighten torment, and improve the general quality of life. Clotting calculated substitution treatment is a foundation of treatment, including the organization of clotting figure concentrates to supplement lacking or broken variables. The recurrence and dose of mixtures are custom-fitted to a person’s needs, taking into account variables such as age, weight, and seriousness of the condition. To assist in diminishing dying terms, antifibrinolytic solutions may be endorsed. A comprehensive torment administration arrangement, consolidating physical treatment, word-related treatment, and pharmacological intercessions, makes a difference in moderating joint torment and moving forward portability. Normal observing of clotting figure levels, joint well-being, and by and large well-being is fundamental to altering treatment plans in like manner. In a few occasions, surgical intercessions may be essential to repair or supplant harmed joints. Additionally, embracing way-of-life alterations such as dodging high-risk exercises, keeping up a solid weight, and remaining hydrated can altogether contribute to fruitful inherited bleeding disorder administration. Progressing inquiries about and developing medicines, counting quality treatment, offer promising prospects for improving care and moving forward results.
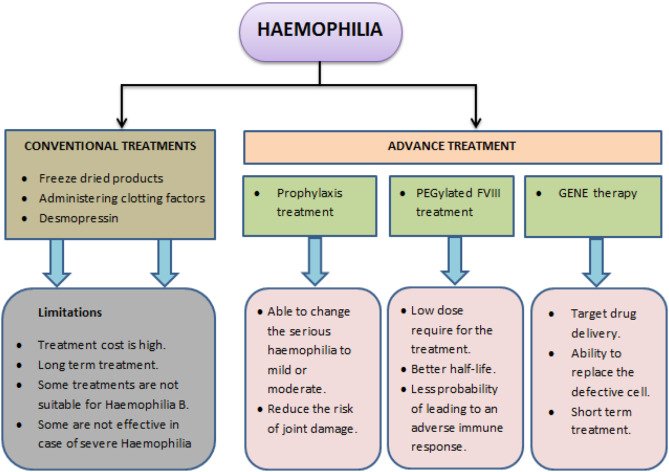
Reference: Advance Treatment
Complications of Hemophilia
Hemophilia can lead to various complications, including chronic joint pain, arthritis, and limited mobility due to frequent bleeding episodes. Life-threatening bleeding in critical organs, infections from contaminated blood products, and the development of inhibitors can also occur. Additionally, individuals with this bleeding disorder are at risk of osteoporosis, mental health concerns, and complications from medical procedures. Effective management and close monitoring by healthcare providers are crucial to mitigate these risks and related conditions.
Bleeding disorders, specifically those characterized by impaired clotting factor function, necessitate a multifaceted approach to management and care. Despite their complexities, advancements in medical research and treatment options have significantly enhanced the quality of life and life expectancy for those affected. By gaining a deeper understanding of the underlying causes, recognizing symptoms, and navigating diagnosis, treatment, and potential complications, individuals and families impacted by inherited bleeding conditions can better cope with their effects. Ongoing research and support hold the promise of further improving the lives of those living with these conditions, bringing us closer to a potential cure and a brighter future.