HIV, or Human Immunodeficiency Infection, is a viral contamination that targets the body’s resistant framework, particularly the CD4 cells too known as T cells. Over time, HIV slowly debilitates the safe framework, making the body more vulnerable to deft contaminations and illnesses. This viral disease can be transmitted through different real liquids, counting blood, semen, vaginal and rectal liquids, and breast drain. HIV can be controlled and overseen as a constant condition, permitting people to lead dynamic and solid lives. HIV is the virus, AIDS is the condition that results from untreated HIV.
AIDS, or Procured Immunodeficiency Disorder, is a condition that happens when HIV has seriously compromised the resistant framework, making the body helpless to a run of astute contaminations and infections. This ordinarily happens when the CD4 cell number drops underneath 200 cells per cubic millimeter of blood or when certain artful contaminations are show. Helps is a late-stage sign of HIV disease, showing that the infection has advanced and the resistant framework is seriously harmed. Forceful treatment and administration are fundamental to avoid assisting harm, make strides in quality of life, and oversee the condition successfully.
Reference: HIV Basics
Causes and Transmission
HIV contamination happens when the Human Immunodeficiency Infection (HIV) assaults and debilitates the body’s resistant framework. If cleared out untreated, HIV can advance to Obtained Immunodeficiency Disorder (Helps), an extreme and life-threatening condition.
People can transmit HIV through different implies, including:
- Locks in unprotected sex with a contaminated accomplice, which permits the infection to enter the body through mucous membranes
- Sharing needles or infusion hardware with somebody who has HIV, which exchanges the infection specifically into the bloodstream
- Receiving contaminated blood transfusions, although this is rare in developed nations with rigorous blood screening protocols in place.
- Mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding, which healthcare providers can prevent with proper treatment and care.
Additionally, individuals can increment their hazard of HIV transmission by:
- Sharing individual care things like razors, toothbrushes, or nail clippers with somebody who has HIV
- Getting tattoos or piercings with unsterilized equipment
- Locks in high-risk behaviors like sharing needles or having unprotected sex with different partners
To anticipate HIV transmission, people can take the taking after steps:
- Utilize condoms and greases accurately amid sex
- Get tried for HIV and get treatment if infected
- Utilize sterile needles and equipment
- Maintain a strategic distance from high-risk behaviors
Symptoms and Diagnosis
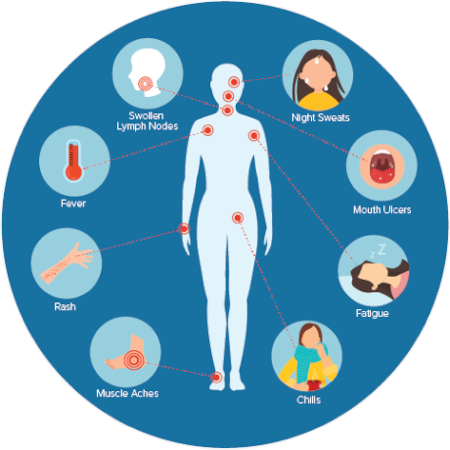
When HIV contaminates the body, it can trigger a run of early indications, such as fever, chills, hasty, night sweats, weakness, swollen lymph hubs, sore throat, mouth ulcers, muscle hurts, and joint torment. These indications regularly develop within 2-4 weeks after contamination and can final for a few weeks. As HIV advances, it can cause more serious side effects, such as persistent runs, weight misfortune, weariness, swollen lymph hubs, skin rashes, yeast contaminations, tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, cryptococcal meningitis, and Kaposi’s sarcoma.
Healthcare experts analyze HIV through a combination of tests and strategies. They utilize HIV counteracting agent tests to identify antibodies against HIV in blood and HIV antigen tests to identify HIV proteins in blood. They moreover utilize PCR (polymerase chain response) tests to distinguish HIV hereditary fabric in blood, CD4 cell tallies to determine the number of CD4 cells, and viral stack tests to degree the sum of HIV in blood. By effectively utilizing these demonstrative instruments, healthcare experts can precisely recognize HIV contaminations and screen their movement.
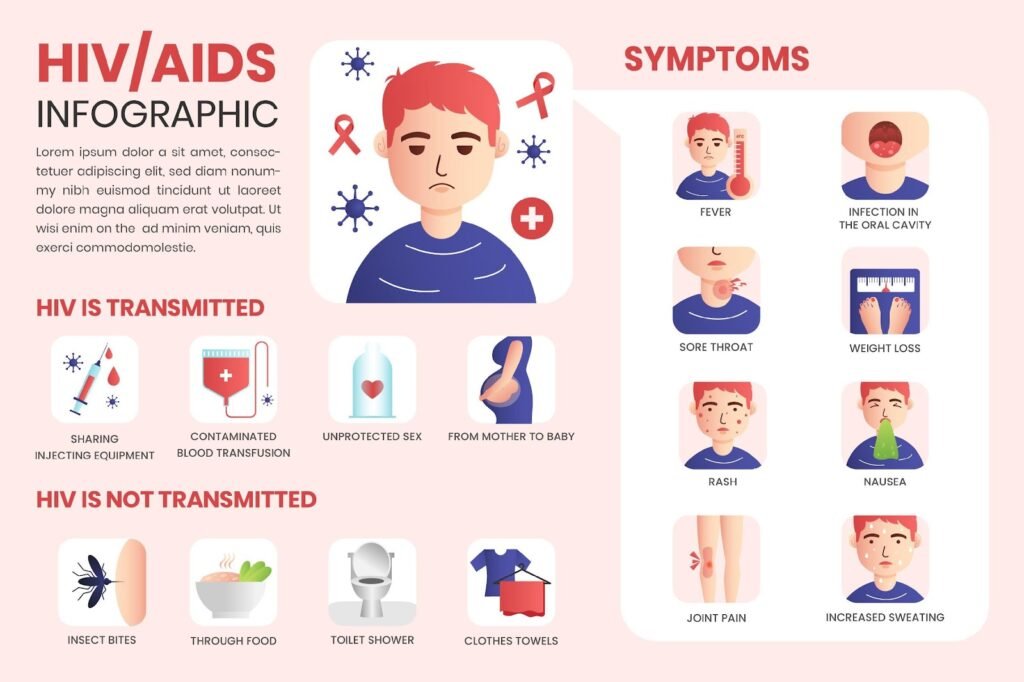
Reference: HIV/AIDS Symptoms
Treatment and Management
HIV treatment includes a multifaceted approach that includes:
- Antiretroviral treatment (Craftsmanship): A combination of solutions that work together to smother the infection and moderate its progression.
- Profoundly Dynamic Antiretroviral Treatment (HAART): A vigorous treatment regimen that combines three or more medicines to maximally stifle the virus.
- Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP): A day-by-day medicine taken by people who are HIV-negative to anticipate infection.
- Post-exposure prophylaxis (Get up and go): A brief course of medicine taken after potential introduction to avoid infection.
Effective administration of HIV moreover involves:
- Customary checking of CD4 cell checks to survey resistant framework function.
- Viral stack tests to degree the sum of HIV in the blood.
- Adherence counseling to back people in taking their drugs correctly.
- Way of life alterations, such as keeping up a solid diet, working out routinely, overseeing stretch, and maintaining a strategic distance from substance abuse.
- Co-infection administration to treat related conditions like tuberculosis, hepatitis, and STIs.
- Mental well-being back to address discouragement, uneasiness, and other mental concerns.
- Social bolster to interface people with assets, back bunches, and community services.
The essential objectives of HIV treatment are to:
- Accomplish viral concealment by diminishing HIV to imperceptible levels.
- Reestablish resistant work by expanding CD4 cell counts.
- Avoid bits of help by halting malady progression.
- Make strides in quality of life by improving physical and mental well-being.
Prevention and Education
HIV avoidance and instruction are pivotal in the battle against the illness, and viable anticipation strategies such as reliable condom utilization, pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) pharmaceutical, post-exposure prophylaxis (Energy) medicine, secure needle get to, and customary HIV testing can essentially diminish transmission. In addition, instruction and mindfulness play an imperative part in anticipating the spread of HIV, and understanding how HIV is transmitted. Furthermore, decreasing shame and advancing understanding can be accomplished by cultivating sympathy, sharing individual stories, giving exact data, supporting influenced communities, and making comprehensive situations. Eventually, by combining these endeavors, we can work towards a future with zero unused HIV contaminations, zero AIDS-related passing’s, making a world where HIV is a reasonable condition that permits people to live long, sound lives.

Reference: AIDS/HIV Prevention
HIV/AIDS is a complex and multifaceted infection that requires a comprehensive approach to anticipation, treatment, and administration. Through instruction, mindfulness, and community engagement, we can diminish disgrace and advance understanding, eventually working towards a future with zero unused HIV diseases, zero AIDS-related passings, and zero separation. By combining viable anticipation strategies, antiretroviral treatment, and worldwide endeavors, we can oversee HIV as a constant condition, progress quality of life, and make a world where HIV is no longer a life-threatening illness. It is fundamental that we proceed to bolster investigate, backing, and community-based activities to accomplish this vision and guarantee a more beneficial future for all.