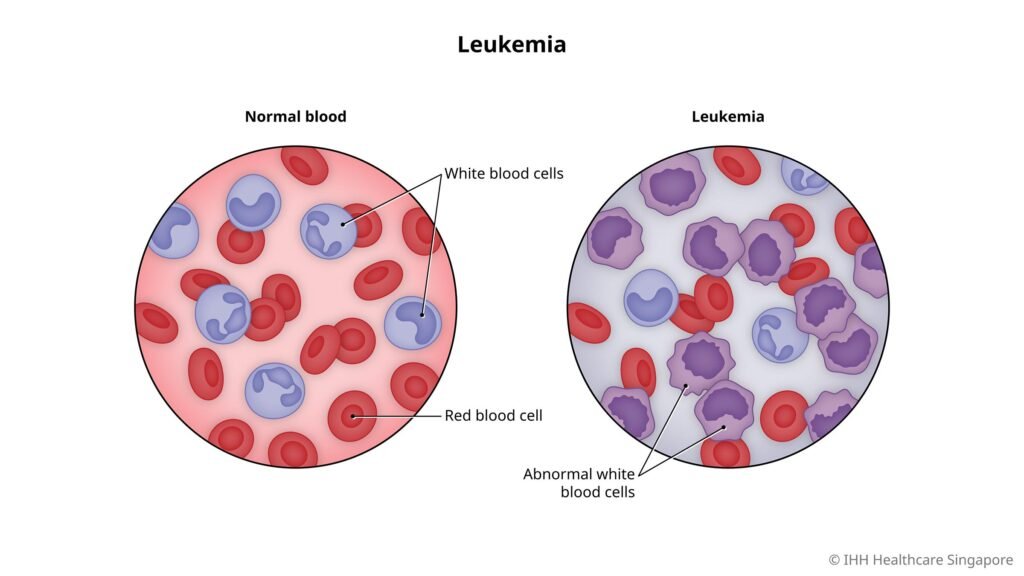
Leukemia is an intricate and multifaceted disease that impacts the blood and bone marrow, critical components of our immune system and overall well-being. It arises when the bone marrow, responsible for producing blood cells, malfunctions, leading to the uncontrollable growth of abnormal white blood cells. These anomalous cells, known as leukemic cells, accumulate in the bone marrow, blood, and other tissues, causing a range of complications. As the leukemic cells proliferate, they displace healthy cells, disrupting normal bodily functions and leading to issues such as anemia, infection, bleeding, and organ damage. This complex disease requires a comprehensive understanding of its underlying mechanisms, symptoms, and treatment options to effectively manage and combat it.
Reference: Blood Cancer
Types of Leukemia
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): A fast-growing cancer of the lymphoid cells, most common in children and young adults.
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): A fast-growing cancer of the myeloid cells, most common in adults.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): A slow-growing cancer of the lymphoid cells, most common in older adults.
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): A slow-growing cancer of the myeloid cells, most common in adults.
- Hairy Cell Leukemia (HCL): A rare, slow-growing cancer of the lymphoid cells.
- T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (T-ALL): A fast-growing cancer of the T-cells.
- B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-ALL): A fast-growing cancer of the B-cells.
- Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL): A fast-growing cancer of the myeloid cells.
- Mixed Lineage Leukemia (MLL): A rare, fast-growing cancer of the lymphoid and myeloid cells.
- Undifferentiated Leukemia: A rare, fast-growing cancer that doesn’t fit into other categories.
Causes and Risk Factors
The beginnings of leukemia are complex and multifaceted, with different variables contributing to its advancement. Hereditary modifications, for occurrence, can disturb ordinary cellular work, leading to the rise of leukemia. Essentially, introduction to destructive radiation, whether through natural mishaps or therapeutic medicines, can moreover trigger the onset of this disease.
Additionally, certain natural poisons, such as benzene, have been connected to an expanded hazard of leukemia. Contaminations with particular infections, like HTLV-1, can moreover incline people to this condition. Progressing age is another critical hazard calculated, with the probability of creating cancer expanding significantly after the age of 55. Family history also plays a part, with people having a first-degree relative with leukemia confronting a higher chance of creating the disease.
Other hazard components incorporate an earlier introduction to cancer medications like chemotherapy and radiation treatment, which can accidentally increase the probability of leukemia. Smoking has moreover been distinguished as a chance figure, especially for certain subtypes of leukemia. Certain hereditary conditions, such as Down disorder, can moreover raise the hazard of creating leukemia. Delayed presentation to unsafe chemicals, like pesticides and mechanical solvents, can too contribute to the advancement of this illness. In conclusion, a compromised safe framework, whether due to basic therapeutic conditions or immunosuppressive treatments, can moreover increment helplessness to leukemia.

Reference: Causes and Risk Factors
Symptoms
Early Symptoms:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Unexplained weight loss
- Recurring infections
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Swollen lymph nodes
Advanced Symptoms:
- Anemia (leading to pale skin and shortness of breath)
- Bleeding or bruising easily
- Tiny red spots on the skin (petechiae)
- Swollen liver or spleen
- Joint pain or swelling
- Abdominal discomfort
Type-Specific Symptoms:
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL):
- Bone pain
- Headaches
- Vomiting
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML):
- Gum bleeding
- Nosebleeds
- Skin infections
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL):
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML):
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Night sweats
Diagnosis of Leukemia
The diagnosis of leukemia includes a comprehensive assessment, beginning with a physical examination and therapeutic history to distinguish potential signs and hazard components, taken after by blood tests, counting a total blood number, blood chemistry tests, and blood spread, to evaluate blood cell tallies and distinguish variations from the norm. A bone marrow biopsy is too vital, including the collection of bone marrow tissue for tiny examination, whereas imaging tests like X-rays, CT filters, and MRI offer assistance assess inner organs and identifying bone or joint harm. Also, cytogenetic examination and atomic testing recognize chromosomal anomalies and particular hereditary transformations, all of which are basic to precisely analyze blood cancer, direct treatment choices, and educate guess, despite the challenges of asymptomatic early stages and comparable indications to other conditions.
Treatment of Leukemia
Treatment for blood cancer is custom fitted to the particular sort and arrange of the infection, as well as the individual’s by and large well-being. Chemotherapy, which includes utilizing solutions to murder cancer cells, is frequently utilized in conjunction with other medicines. Focused on treatment, another approach, centers on particular atomic variations from the norm to stop cancer development. In a few cases, stem cell transplantation may be fundamental, where sound stem cells supplant harmed bone marrow. Immunotherapy, which boosts the safe framework to battle cancer cells, is also a choice. Also, radiation treatment, which utilizes high-energy radiation to crush cancer cells, may be utilized. The choice of treatment depends on different variables, and a healthcare proficient will decide the most compelling approach for each person’s case, frequently combining numerous medications to accomplish the best conceivable result.
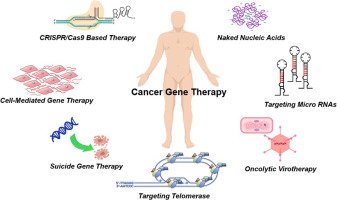
Reference: Current Trends in Cancer Therapy
Eventually, the battle against blood cancer requires a personalized and multifaceted methodology, custom-fitted to each individual’s one-of-a-kind needs and circumstances. By shedding light on the complexities of this infection, counting its different shapes, caution signs, symptomatic pathways, and treatment modalities, we can engage those influenced to take control of their well-being and make educated choices around their care. As the therapeutic investigation proceeds to progress, we can see forward to made strides in results and a more confident future for those affected by this impressive illness.