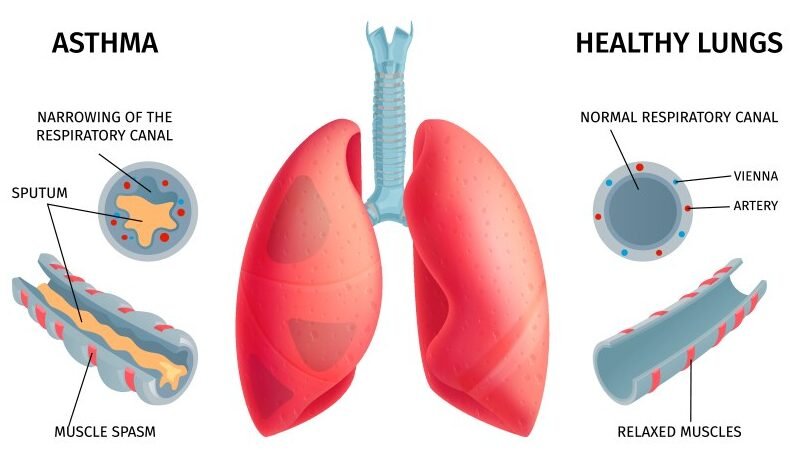
Asthma is a inveterate respiratory condition characterized by repeating scenes of aviation route hindrance, irritation, and fit. This complex malady influences the aviation routes, causing them to contract and swell, driving to indications like wheezing, hacking, chest snugness, and shortness of breath. Asthma’s affect on breathing can be serious, altogether impeding every day life. With its predominance on the rise, this chronic respiratory condition influences millions around the world, making it a critical open wellbeing concern. In spite of its broad affect, asthma remains a reasonable condition, and with legitimate treatment and self-management methodologies, people can viably control side effects, avoid exacerbations, and lead dynamic lives

Reference: Asthma
Causes and Triggers
A. Asthma Triggers
1. Allergenic Substances
– Infinitesimal tidy bugs in bedding and carpets
– Dust from trees, grasses, and weeds
– Proteins in pet dander and saliva
– Shape spores in soggy environments
– Cockroach squander products
2. Bothering Agents
– Tobacco smoke and used smoke
– Discuss toxins like particulate matter and ozone
– Solid chemicals in family cleaners
– Scents in individual care products
– Vapor from paint and building materials
3. Respiratory Infections
– Viral and bacterial contaminations like the common cold and flu
– Sinus diseases and bronchitis
4. Physical Stimuli
– Strenuous work out and physical activity
– Stretch and passionate anxiety
– Hormonal changes amid feminine cycle and pregnancy
5. Natural Factors
– Changes in climate and temperature
– Cold discuss and wind
B. Chance Variables for Creating Asthma
1. Hereditary Susceptibility
2. Family Therapeutic History
3. Unfavorably susceptible Conditions like Dermatitis and Roughage Fever
4. Early Childhood Respiratory Infections
5. Presentation to Tobacco Smoke and Discuss Pollution
6. Corpulence and Being Overweight
7. Untimely Birth and Moo Birth Weight
8. Certain Drugs like Ibuprofen and NSAIDs
Symptoms
Asthma’s side effects can be weakening, affecting every day life in noteworthy ways. Firstly, wheezing and hacking are common complaints, regularly went with by chest snugness and shortness of breath. As side effects raise, breathing gets to be progressively labored, driving to weakness and laziness. Also, asthma assaults can strike at any time, activated by allergens, aggravations, or push. In the mean time, nighttime side effects can disturb rest designs, causing advance weariness. Moreover, asthma’s affect on lung work can lead to fast pulse, uneasiness, and freeze. Subsequently, recognizing these indications is significant for variable administration and treatment.

Reference: Signs and Symptoms
Diagnosis
Asthma diagnosis involves a comprehensive approach, combining medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Initially, healthcare providers assess symptoms, medical background, and lifestyle factors to identify potential triggers. Next, a thorough physical examination, including lung function tests, helps determine the severity of symptoms. Spirometry, a key diagnostic tool, measures lung function, revealing airflow obstruction and reversibility. Additionally, methacholine challenge tests may be conducted to assess airway responsiveness. Furthermore, allergy tests, such as skin prick tests or blood tests, can identify specific allergens contributing to symptoms. Finally, healthcare providers consider alternative diagnoses, ensuring an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan.
Treatment and Management
Compelling asthma administration includes a multi-faceted approach, combining solutions, way of life adjustments, and shirking of triggers. Drugs such as breathed in corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and combination inhalers frame the foundation of treatment, making a difference to control indications and anticipate exacerbations. In the interim, way of life changes like stopping smoking, keeping up a sound weight, and locks in in normal work out can essentially progress side effects. Moreover, recognizing and dodging triggers like allergens, aggravations, and stretch is pivotal for effective administration. Moreover, creating a personalized activity arrange empowers people to screen indications, alter medicines, and look for restorative consideration when fundamental. By receiving a proactive and educated approach, people with asthma can lead dynamic, symptom-free lives.
Types of Asthma
Asthma presents in diverse forms, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of its various types.
A. Severity Spectrum
- Mild Asthma: Infrequent and mild symptoms with minimal daily impact.
- Moderate Asthma: Regular symptoms with some daily limitations.
- Severe Asthma: Persistent and intense symptoms significantly impairing daily life.
B. Distinct Categories
- Exercise-Induced Asthma: Physical activity triggers bronchospasm.
- Occupational Asthma: Workplace exposures to allergens or irritants provoke symptoms.
- Allergic Asthma: Specific allergens like dust mites, pollen, or pet dander trigger symptoms.
- Non-Allergic Asthma: Symptoms unrelated to allergens, often linked to respiratory infections or irritants.
- Cough-Predominant Asthma: Persistent coughing as the primary manifestation.
- Nocturnal Asthma: Symptoms intensify at night, disrupting sleep patterns.
- Treatment-Resistant Asthma: Symptoms persist despite standard treatments.
Asthma in Specific Population
Asthma’s impact varies across different populations, necessitating tailored approaches to care.
In pediatric patients, asthma often manifests as wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath, requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent long-term lung damage and ensure normal growth and development. As children’s asthma evolves, regular monitoring and adjustments to treatment plans are crucial.
Adults with asthma may experience a distinct set of challenges, including comorbidities like allergies, sinusitis, or gastroesophageal reflux disease, which can complicate management. Effective treatment involves addressing these comorbidities and developing personalized plans to manage symptoms, prevent exacerbations, and improve quality of life.
During pregnancy, asthma management is critical to ensure the health and well-being of both mother and fetus. Hormonal fluctuations can influence this chronic respiratory condition symptoms, and uncontrolled asthma can increase the risk of preterm labor, low birth weight, and other complications. A collaborative approach between obstetricians and allergists is essential to develop safe and effective treatment plans, minimizing risks and promoting a healthy pregnancy.

Reference: Anatomy of Asthma
managing chronic airway inflammation requires a multifaceted strategy that addresses the complex interplay of symptoms, triggers, and lifestyle factors. By adopting a tailored approach that incorporates evidence-based treatments, behavioral modifications, and environmental adjustments, individuals can effectively mitigate the impact of this respiratory condition and improve their overall well-being. Ongoing research and advancements in therapeutic options offer promising prospects for enhanced symptom control, improved quality of life, and renewed hope for those navigating the challenges of chronic respiratory disease.