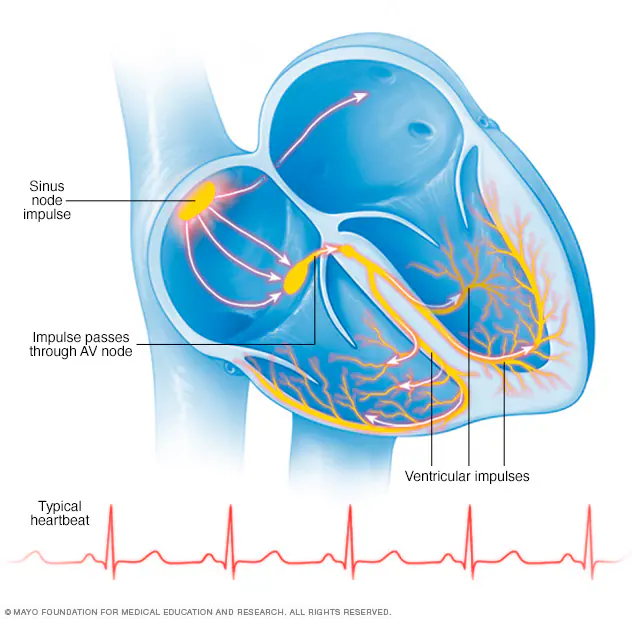
An arrhythmia is a complex heart condition characterized by an anomalous pulse, where the heart’s normal cadence is disturbed, causing it to beat as well rapidly, as well gradually, or unpredictably. This disturbance happens when the electrical motivations that direct the pulse breakdown or gotten to be disturbed, driving to a deviation from the heart’s ordinary cadence. As a result, the heart may beat as well quick, a condition known as tachycardia, or as well moderate, known as bradycardia, or it may beat sporadically, causing an unusual and possibly life-threatening beat. Understanding arrhythmias is vital, as they can run from mellow and safe to extreme and possibly lethal, making exact conclusion and treatment basic to avoid complications and move forward quiet results.

Reference: Heart Arrhythmia
Types of Arrhythmias
Tachycardia:
A quick pulse surpassing 100 beats per diminutive, frequently activated by push, uneasiness, or basic therapeutic conditions like hyperthyroidism or cardiovascular infection. Indications incorporate palpitations, shortness of breath, and dizziness.
Bradycardia:
A moderate pulse underneath 60 beats per diminutive, which may be ordinary for competitors or show an fundamental condition like hypothyroidism, electrolyte lopsidedness, or heart piece. Side effects incorporate weakness, shortcoming, and lightheadedness.
Atrial Fibrillation:
A trembling or sporadic pulse in the upper chambers, expanding stroke chance due to blood clot arrangement. Side effects incorporate palpitations, shortness of breath, and weakness. Atrial fibrillation can be paroxysmal (discontinuous), determined, or permanent.
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT):
A fast pulse beginning in the lower chambers, possibly life-threatening if cleared out untreated. Indications incorporate palpitations, chest torment, and shortness of breath. VT can deteriorate into ventricular fibrillation, requiring quick restorative attention.
Ventricular Fibrillation (VF):
A chaotic, life-threatening pulse requiring prompt therapeutic consideration. VF can cause cardiac capture, driving to sudden cardiac passing if not treated instantly with CPR and defibrillation.
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT):
A quick pulse beginning over the lower chambers, regularly caused by electrical issues like Wolff-Parkinson-White disorder or atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia. Indications incorporate palpitations, shortness of breath, and dizziness.
Long QT Syndrome:
A heart condition causing unpredictable heartbeats, expanding the chance of sudden cardiac passing due to ventricular arrhythmias. Indications incorporate blacking out, seizures, and sudden cardiac arrest.
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome:
A uncommon condition causing a fast pulse due to an additional electrical pathway between the upper and lower chambers. Indications incorporate palpitations, shortness of breath, and chest torment. WPW increments the chance of atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia.
Reference: Types
Causes and Risk Factors
Fundamental Heart Conditions:
- Coronary course illness: Limited or blocked supply routes can disturb heart work, driving to arrhythmias.
- Cardiomyopathy: Heart muscle harm or shortcoming can cause anomalous heart rhythms.
- Heart valve issues: Breaking down valves can influence blood stream, expanding the chance of arrhythmias.
Electrolyte Imbalances:
- Potassium levels: Tall or moo levels can influence heart work, driving to arrhythmias.
- Sodium levels: Lopsided characteristics can disturb heart rhythm.
- Magnesium levels: Lacks can contribute to arrhythmias.
Medications:
- Certain anti-microbials and antihistamines
- Anti-arrhythmic solutions (incidentally, can now and then cause arrhythmias)
- Decongestants and asthma medications
Lifestyle Factors:
- Stretch: Drawn out stretch can increment heart rate and blood weight, contributing to arrhythmias.
- Caffeine: Over the top utilization can fortify the heart, driving to arrhythmias.
- Liquor: Overwhelming drinking can harm the heart, expanding the hazard of arrhythmias.
- Need of rest: Weakness can contribute to arrhythmias.
Genetic Predisposition:
- Family history: Acquired conditions like long QT disorder or Brugada disorder can increment the hazard of arrhythmias.
- Hereditary changes: Certain changes can influence heart work, driving to arrhythmias.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Arrhythmias can show in different ways, and their side effects may extend from mellow to serious. A few people may involvement palpitations, which are sensations of skipped beats or unpredictable heartbeats. Others may feel woozy, mixed up, or brief of breath due to decreased blood stream. Chest torment, weakness, and shortcoming are moreover common side effects. In a few cases, arrhythmias may not display any recognizable indications, making determination challenging.
Diagnosing arrhythmias regularly includes a combination of physical examination, restorative history, and symptomatic tests. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a essential apparatus for identifying arrhythmias, as it records the heart’s electrical movement. Holter observing, a 24-hour convenient ECG, can offer assistance distinguish discontinuous arrhythmias. Echocardiograms, push tests, and electrophysiology thinks about may too be utilized to decide the fundamental cause of the arrhythmia. In a few cases, a cardiac occasion screen or implantable circle recorder may be utilized to identify arrhythmias over an amplified period. Precise determination is vital for creating an successful treatment arrange and overseeing arrhythmias.
Treatment Options
Arrhythmia treatment regularly includes a combination of therapeutic intercessions and way of life adjustments. At first, healthcare suppliers may endorse drugs such as anti-arrhythmic specialists and beta blockers to stabilize the pulse and lighten indications. If these measures are ineffectual, electrical cardioversion may be utilized to reestablish a ordinary cardiac rhythm.
In a few cases, a negligibly obtrusive strategy called catheter removal may be prescribed to dispose of irregular electrical pathways. For people with serious arrhythmias, implantable gadgets like pacemakers and cardioverter-defibrillators may be vital to direct the pulse and anticipate life-threatening complications. Concurrently, receiving a sound way of life is vital for successful arrhythmia administration. This incorporates keeping up a adjusted count calories, locks in in normal physical action, and actualizing stress-reducing techniques.
By coordination these treatment approaches, people with arrhythmias can accomplish ideal results and upgrade their in general well-being. Through a collaborative exertion between healthcare suppliers and patients, personalized treatment plans can be created to address the special needs of each person.

Reference: Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation
Arrhythmias show a complex challenge to heart wellbeing, but with advanced restorative progressions and personalized treatment approaches, people can viably oversee their condition and moderate its affect on every day life. By getting a handle on the fundamental causes, recognizing side effects, and investigating accessible treatment alternatives, those influenced by arrhythmias can engage themselves to take charge of their cardiovascular well-being. Through a collaborative exertion with healthcare experts and proactive way of life alterations, it is conceivable to minimize complications and appreciate an progressed quality of life in spite of the nearness of arrhythmia. By prioritizing proactive heart care and looking for opportune restorative consideration, people can clear the way for a more grounded, more flexible heart.