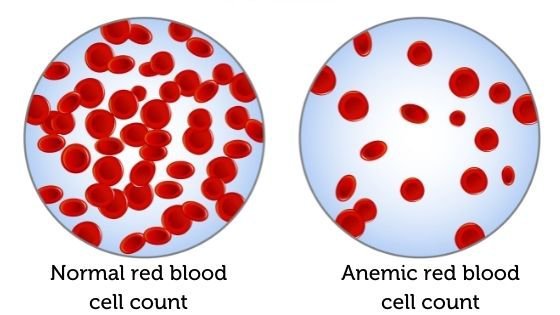
Anemia is an inescapable well-being issue that influences a noteworthy parcel of the worldwide populace, regularly going unnoticed until its side effects weaken. As a condition that can steadily dissolve vitality levels and in general, well-being, understanding iron deficiency is pivotal for successful administration and treatment. At its center, frailty is a blood clutter characterized by insufficient ruddy blood cells or hemoglobin, the protein capable of shipping oxygen to the body’s tissues and organs. When this imperative handle is disturbed, the body’s cells and organs are denied the oxygen they require to work ideally, leading to side effects and potential complications. By getting a handle on the basics of frailty, people can take the to begin with a step towards relieving its effect and reestablishing their body’s oxygen supply.
Reference: Anemia
Types of Anemia
Iron-Deficiency Anemia
- Caused by deficient press in the body
- Leads to lacking ruddy blood cell production
- Can happen due to destitute eating less, intemperate dying, or impeded press absorption
Vitamin Lack Anemia
- Caused by a need for fundamental vitamins (B12 and folate)
- Imperative for ruddy blood cell production
- Can lead to weariness, shortcomings, and shortness of breath
Anemia of Chronic Disease
- Caused by unremitting illnesses (kidney illness, cancer, HIV/AIDS)
- Checked by diminished ruddy blood cell generation due to diligent inflammation
- Challenging to oversee, as it’s regularly an indication of a fundamental condition
Sickle Cell Anemia
- Hereditary clutter influencing hemoglobin production
- Unusually molded ruddy blood cells inclined to breakdown
- Repeating scenes of torment, weakness, and expanded infections
Thalassemia
- Hereditary clutter influencing hemoglobin production
- Ineffectual or annihilated ruddy blood cells
- Can lead to weariness, shortcomings, and bone deformations if cleared out untreated
Causes and Risk Factors
Awakening to the causes and risk factors of anemia reveals a multifaceted landscape. Nutrient deficiencies, particularly iron and vitamins, can trigger this condition. Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, cancer, and HIV/AIDS, can also precipitate anemia. Genetic disorders like sickle cell anemia and thalassemia can be a root cause. Blood loss, whether due to heavy menstrual periods, internal bleeding, or surgical interventions, can further exacerbate the risk. Moreover, specific medications, including NSAIDs, antibiotics, and chemotherapy, can contribute to the development of anemia.
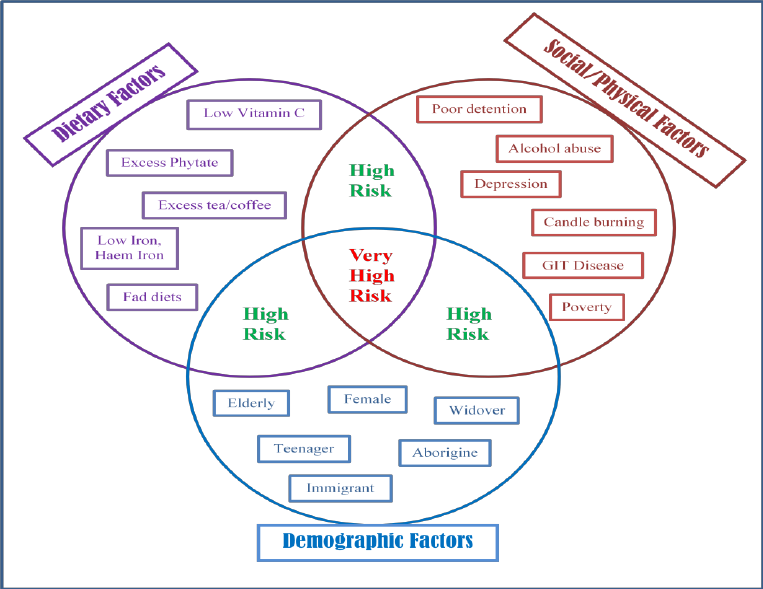
Vulnerability to anemia can be heightened by various factors, including age, dietary choices, and medical history. Older adults, pregnant women, and children are more susceptible to anemia’s grasp. A plant-based diet, if not meticulously planned, can also increase the risk. Individuals grappling with chronic diseases, such as kidney disease, cancer, or HIV/AIDS, are more likely to encounter anemia. Family history can also play a role, as certain genetic disorders can elevate the risk. Additionally, specific ethnic groups, including African Americans, Hispanics/Latinos, and Southeast Asians, are more prone to anemia. Pregnant women, especially those with multiple pregnancies, are also more vulnerable. Heavy menstrual periods or prolonged bleeding can further increase the risk, as can recent surgery or a history of surgical blood loss.
Reference: Risk Factors
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Anemia’s nearness is regularly checked by a cluster of side effects, counting tireless weakness and shortcomings, shortness of breath, and pale skin. Migraines, discombobulation, and wooziness may too happen, went with by cold hands and feet. A diminish in craving, hair misfortune, and fretful leg disorder can assist flag the condition.
Diagnosing iron deficiency includes a comprehensive approach, beginning with a Total Blood Number (CBC) test to degree ruddy blood cell check, hemoglobin, and hematocrit levels. A physical examination takes after, checking for unmistakable signs such as pale skin, fast pulse, and shortness of breath. A exhaustive restorative history is moreover basic to distinguish fundamental conditions or hazard components. Extra blood tests decide press, vitamin B12, and folate levels, whereas a stool test identifies blood misfortune. In a few cases, imaging tests like ultrasound or CT checks may be essential to run the show-out inner bleeding.
A conclusion of frailty is affirmed when hemoglobin levels drop below 13.5 g/dL for men and 12 g/dL for ladies, or when hematocrit levels drop underneath 41% for men and 36% for ladies. Ruddy blood cell numbers underneath 4.32 million cells per microliter assist bolsters the determination. It’s imperative to note that symptomatic criteria may shift depending on the particular sort of frailty and person’s well-being components.
Treatment and Management
Viable Treatment Alternatives for Anemia:
- Press supplementation treatment: A focused on approach to renew press stores and lighten iron-deficiency anemia.
- Vitamin renewal: Tending to fundamental vitamin insufficiencies, such as B12 or folate, to bolster sound ruddy blood cell production.
- Blood transfusion mediation: A restorative strategy to reestablish ruddy blood cells in extreme cases of anemia.
- Comprehensive condition administration: Treat basic therapeutic conditions, like kidney illness or rheumatoid joint pain, to relieve anemia’s impact.
- Personalized dietary arranging: Fitting wholesome admissions to boost press and vitamin levels, counting joining iron-rich foods.
Anemia Administration: All-encompassing Approach
- Nonstop checking and assessment: Standard blood tests to track hemoglobin and pressure levels, illuminating treatment adjustments.
- Way of life optimization: Receiving sound propensities, such as direct workout, adjusted eating less, and push administration, to back by and large well-being.
- Stretch lessening strategies: Investigating mindfulness hones, like reflection or yoga, to minimize stress’s effect on anemia.
- Medicine administration and optimization: Frequently checking on and altering solutions to avoid unfavorable interactions.
- Collaborative care: Planning normal follow-up arrangements with a healthcare supplier to guarantee personalized direction and support.
Reference: Anemia Prevention
Iron deficiency, a multifaceted condition, emerges from an insufficiency in ruddy blood cells or hemoglobin, preventing oxygen conveyance to real tissues. Its different shapes, counting press, and vitamin lack frailty, as well as iron deficiency of incessant malady, stem from a complex interaction of components, including supplement insufficiencies, unremitting conditions, hereditary inclinations, and blood misfortune. Characterized by inconspicuous however weakening indications such as diligent weariness, shortcoming, pale complexion, and shortness of breath, iron deficiency requires a comprehensive symptomatic approach. Compelling administration includes a custom-made procedure, consolidating supplements, blood transfusions, and tending to basic conditions, nearby way of life alterations, and an adjusted count of calories, with progressing checking vital for ideal results and improved well-being.